Architecture Design
Technical White Paper
Bitlayer: A Bitcoin Computational Layer Architecture Based on the BitVM Paradigm
Introduction
Bitlayer has revolutionized the verification process for Layer 2 transactions using optimistic execution, while keeping the Bitcoin protocol intact. Its architecture comprises transaction processing, verification, and asset bridging components. Transaction processing involves a sequencer and a Layered Virtual Machine (LVM), optimizing transaction handling and computational efficiency. Transaction verification, managed by provers and challengers, ensures transaction validity and compliance with network rules. They collaborate to complete the entire process from Layer 2 transaction handling to Layer 1 confirmation, maintaining transaction security and integrity throughout the process. Bitlayer's assets bridge components further enhance its capabilities by enabling interoperability between Layer 2 and Layer 1 networks, facilitating secure asset transfer across blockchain layers.
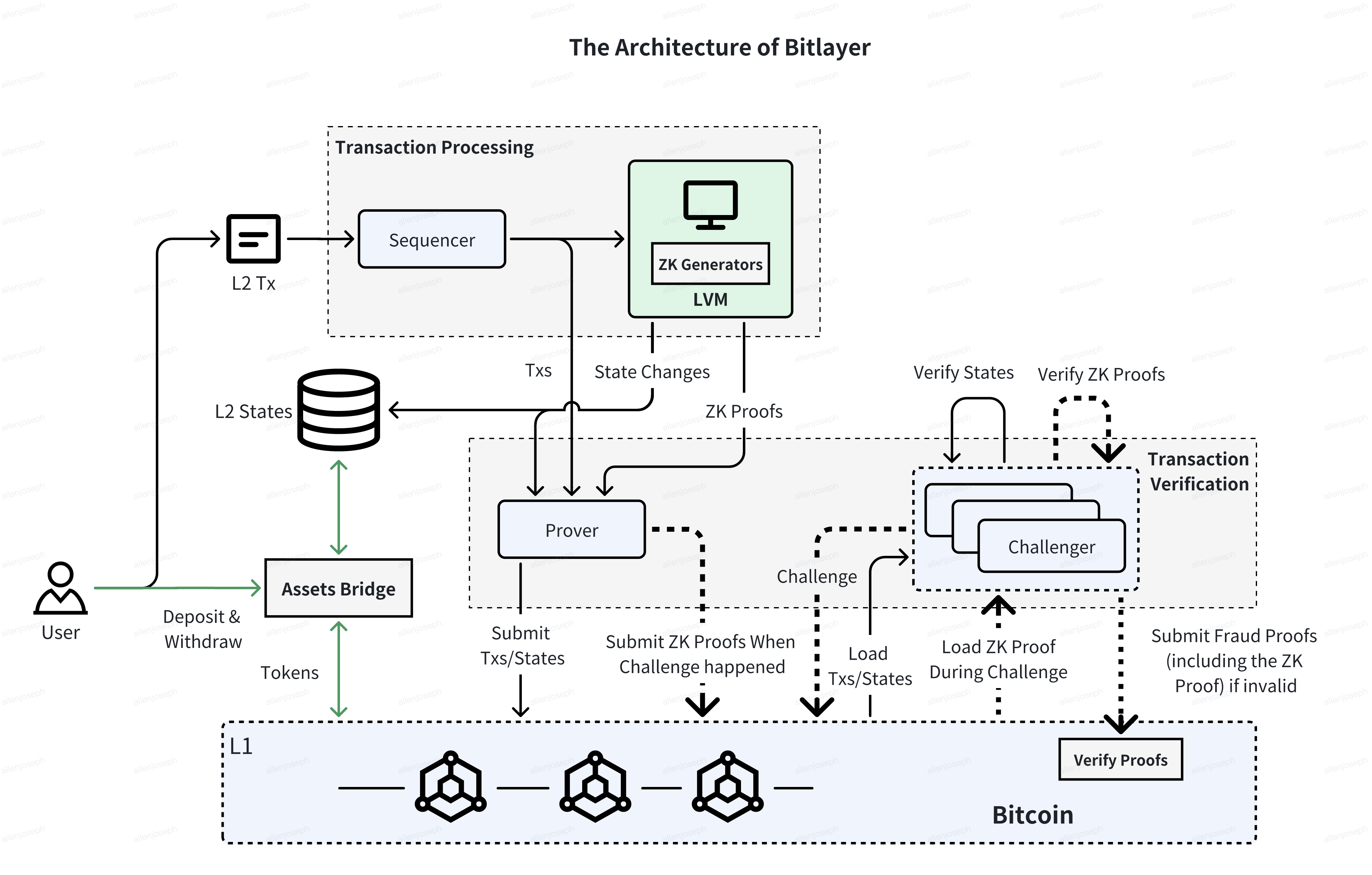
1. Transaction Processing
Transaction Processing, as illustrated in the figure above, involves the sequencer and Layered Virtual Machine. These components are responsible for the entire transaction handling, starting from transaction acceptance to executing the output.
- Sequencer: Like other Layer 2 solutions, the sequencer in Bitlayer is responsible for collecting cached transactions and sorting them, serving as the entry point for transactions in Bitlayer.
- Layered Virtual Machine (LVM): The LVM is the computing component of Bitlayer, responsible for executing smart contracts and generating the latest states and zero-knowledge proof. Challengers then use this proof to challenge the execution results.
2. Transaction Verification
In Bitlayer, transaction verification is achieved by a zero-knowledge-based optimistic mechanism between the prover and challenger.
- Prover: The Prover is responsible for submitting Layer 2 transactions and states of execution to the Layer 1 chain as described above. It also reveals zero-knowledge proofs on the chain when getting challenged.
- Challenger: The Challenger is responsible for verifying the execution results submitted by the Prover through states of execution and zero-knowledge proof verification. If malicious behavior is detected, the Challenger initiates a challenge process to generate fraud proofs including invalid zero-knowledge proofs and submits them to the Layer 1 chain.
3. Asset Bridge
The Bridge acts as a crucial component in Bitlayer's infrastructure, facilitating the seamless movement of assets between Layer 2 and Layer 1. Its primary responsibility is to ensure the secure transfer of user assets through an innovative combination of OP-DLC and BitVM.